Accidents happen, often when we least expect them. Whether it’s a scraped knee on the playground, a kitchen knife slip, or something more serious, knowing how to handle bleeding effectively can make all the difference. The right response can not only prevent further blood loss but also reduce the risk of complications like infection.
This guide is a practical resource for parents, caregivers, and first-aid enthusiasts looking to gain confidence in managing bleeding emergencies. By the end of this post, you’ll understand various types of bleeding, how to control it, and when to seek professional help.
Understanding the Types of Bleeding
Not all bleeding is the same. The approach to handling it may vary depending on the type of injury and affected blood vessels. Here’s a breakdown of the three main types of bleeding, along with examples to help you identify them.
1. Arterial Bleeding
Arterial bleeding involves blood spurting from an artery with each heartbeat. It is bright red and tends to be more dangerous due to the speed and volume of blood loss. This type of bleeding is often seen in life-threatening situations, such as severe lacerations or traumatic injuries.
Example: A deep cut from a power tool could cause arterial bleeding.
2. Venous Bleeding
This occurs when a vein is damaged. The blood flows steadily, is dark red or maroon, and may be easier to control than arterial bleeding.
Example: A deep gash on the leg caused by broken glass can result in venous bleeding.
3. Capillary Bleeding
Capillary bleeding is the least severe and occurs when small blood vessels near the skin's surface are damaged. Blood typically oozes rather than flows.
Example: A scraped knee or a minor paper cut will cause capillary bleeding.
Knowing how to differentiate between these types is critical for appropriately managing the situation and determining urgency.
First Aid QuickMed Pack

$24.95
$29.94
Features: Ripstop nylon bag Handy front pocket, durable carabiner and a handle An essential part of any household or workplace. Designed to efficiently treat burns and injuries. Keep your safety a top priority with this comprehensive pack. … read more
Take Action to Control Bleeding
When bleeding occurs, immediate action is essential. The steps below outline what to do in most cases, regardless of the bleeding’s severity.
Apply Direct Pressure
Use a clean cloth or sterile bandage to press directly on the wound. This helps slow or stop the bleeding by giving the blood vessels time to begin clotting. If the blood soaks through, do not remove the bandage—simply add another layer on top for extra absorption.
Elevate the Wounded Area
If possible, elevate the bleeding area above the heart. This reduces blood flow to the wound and aids clotting. For instance, if the injury is on a person’s arm, prop it up using a pillow while applying pressure.
Apply Pressure to Pressure Points
For severe bleeding, pressing on pressure points—areas where arteries are close to the skin, such as the groin or arm—can reduce blood flow to the injury site.
Quick actions like these can make a significant impact while waiting for additional help or assessing the need for further intervention.
Using a Tourniquet Safely
Tourniquets should only be used as a last resort when direct pressure and elevation are insufficient to control life-threatening bleeding. Improper use may cause additional harm.
Guidelines for Proper Tourniquet Application
- Place the tourniquet 2-3 inches above the wound but not over a joint.
- Tighten until the bleeding stops, and never loosen it once applied.
- Note the time of application. Medical professionals need to know how long it has been in place, as prolonged use can lead to tissue damage.
Remember, tourniquets are life-saving tools when used correctly, but they should only be handled by individuals trained in their application.
Proper Wound Care and Bandaging
Controlling bleeding is only the first step; preventing infection is equally important. Follow these steps to care for the wound post-bleeding.
- Clean the wound using warm water or saline solution to remove debris.
- Avoid using alcohol or hydrogen peroxide, as these can irritate the tissue and slow healing.
- Apply an antibiotic ointment to reduce the risk of infection.
- Cover the wound with a sterile bandage. Ensure it’s secure but not too tight.
Change the bandage daily or if it becomes wet or dirty. Monitoring for signs of infection (such as redness, swelling, or pus) is crucial in ensuring proper healing.
When to Seek Medical Help
Some injuries require immediate medical intervention. Knowing when to go to the emergency room can save lives. Here are some indicators for professional care:
- Bleeding Won’t Stop despite applying direct pressure for 10 minutes.
- Signs of Arterial Bleeding, such as spurting blood.
- Deep Wounds or Embedded Objects that require stitches or surgical removal.
- Signs of Infection, including a fever or red streaks around the wound.
Emergency rooms are equipped to handle severe cases, including stitching wounds, blood transfusions, and monitoring for complications.
Tips to Prevent Bleeding Injuries
Prevention is always better than a cure. Here are proactive steps to create a safer environment and reduce the likelihood of injuries that lead to significant bleeding.
- Childproof Your Space by covering sharp corners, locking away knives, and keeping fragile items out of reach.
- Use Protective Gear when engaging in risky activities like cycling, woodworking, or sports. Helmets, gloves, and knee/elbow pads can significantly reduce injuries.
- Practice Kitchen Safety by using sharp knives carefully, ensuring dry cutting surfaces, and storing tools securely.
By fostering a safety-first mindset, you can minimize risks and create a more secure environment for everyone.
Real-life Scenarios of Effective Bleeding Management
Stories of quick thinking and effective first-aid application can serve as inspiration.
Scenario 1: A mother controlled her child’s bleeding from a bike accident using direct pressure and a clean towel. Her preparedness prevented further blood loss until professional help arrived.
Scenario 2: A hiker applied a tourniquet while waiting for emergency responders after sustaining deep cuts during a fall, effectively saving their life.
These real-life examples emphasize why it’s so important to have basic first-aid knowledge.
First Aid ProMed Pack
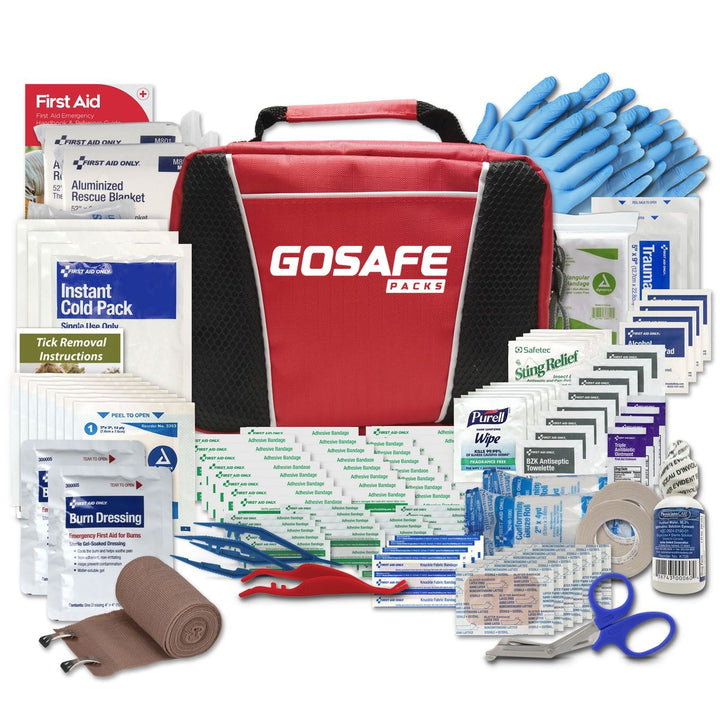

$39.95
$47.94
Features: Be ready for any emergency with the GoSafe ProMed First Aid Pack. Rip Stop Nylon zippered bag Fully equipped with top-quality medical supplies to handle injuries and accidents Safety and peace of mind, always within reach. … read more
Be Prepared to Act Confidently
Bleeding emergencies can be scary, but with the right knowledge and tools, you can turn chaos into calm. By understanding the types of bleeding, acting swiftly, and knowing when to seek professional care, you can significantly improve the outcome of an injury.
Take your preparedness to the next level—enroll in a first-aid course today and discover how confidence in your skills can make all the difference.