Nature can be breathtaking, but it also comes with risks. Whether you're hiking through a forest, camping with family, or embarking on a thrilling outdoor adventure, emergencies like dehydration, hypothermia, or snake bites can happen unexpectedly.
Knowing how to respond could be the key to saving a life—maybe even your own. This quick first aid guide will walk you through essential steps to handle common wilderness emergencies so you can explore with confidence.
Identifying and Treating Dehydration
What is Dehydration?
Dehydration happens when your body loses more water than it takes in, leading to a severe imbalance that can affect your energy, cognition, and overall ability to function. It’s a common issue in outdoor activities, especially during summer hikes or extensive adventures.
Signs of Dehydration:
- Dry mouth and excessive thirst
- Fatigue or dizziness
- Dark urine or infrequent urination
- Confusion and irritability (in severe cases)
First Aid Steps for Dehydration
- Stop and Rest: Seek shade or move to a cool environment immediately.
- Rehydrate Gradually: Sip water slowly rather than gulping to avoid nausea. If available, opt for electrolyte-rich drinks to replenish salts and minerals. Avoid caffeine or alcohol, as they can worsen dehydration.
- Monitor Symptoms: Observe whether symptoms improve. If dehydration becomes severe (e.g., fainting or confusion), it’s time to seek immediate help by contacting emergency services.
Prevention Tip: Always pack more water than you think you’ll need, and take breaks to hydrate consistently on your trip, even if you don’t feel thirsty.
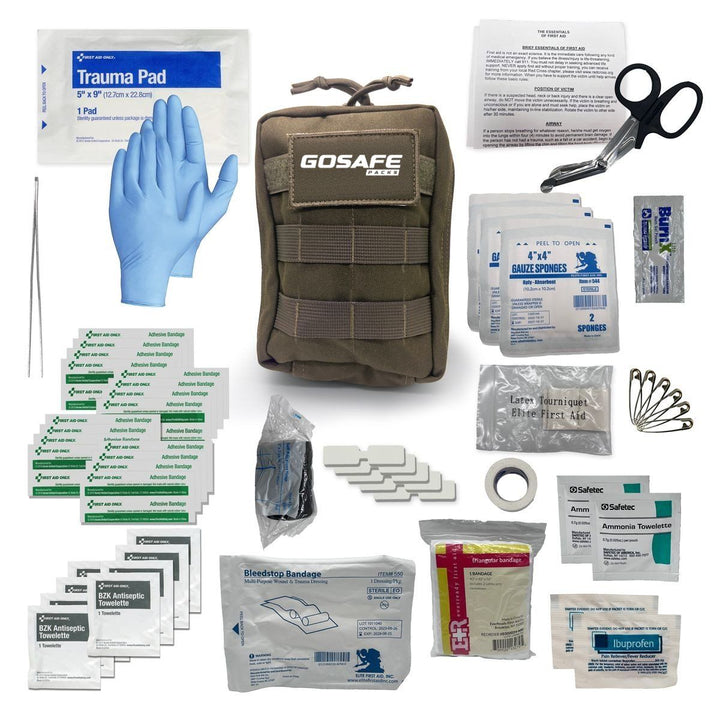
First Aid Survival Pack
$69.95
$130.00
Essential basic trauma supplies. Designed by a former para-rescue team, this kit is ideal for police, military, tactical groups, and hunters who may find themselves in high-risk situations. Easy access to all essential items during emergencies. … read more
Handling Hypothermia in Cold Environments
What is Hypothermia?
Hypothermia occurs when your body loses heat faster than it can produce it, resulting in a dangerously low body temperature. It often happens in cold, wet conditions or when you’re exposed to freezing temperatures without adequate insulation.
Signs of Hypothermia:
- Shivering, which may later stop as it worsens
- Slurred speech or inability to think clearly
- Clumsiness and lack of coordination
- Slow, shallow breathing
First Aid Steps for Hypothermia
- Get Out of the Cold: Move the individual to a dry shelter or tent. Remove any wet clothing and replace it with dry, insulated layers or a thermal blanket.
- Warm the Core First: Warm their chest, neck, and head using body heat, warm packs, or dry clothing. Avoid rubbing cold skin, as this can cause further damage.
- Offer Warm (Non-Alcoholic) Drinks: Provide warm liquids like tea or soup, but skip alcohol as it lowers body temperature further.
- Emergency Care: If the person is unconscious or showing severe symptoms, seek help immediately or activate your emergency beacon.
Prevention Tip: Dress in layers, including moisture-wicking clothing to stave off sweat, and always carry an emergency blanket in your pack!
Responding to Snake Bites
The Danger of Snake Bites
Despite being rare, snake bites can occur while exploring the wilderness, particularly in areas with diverse wildlife. Most bites are defensive, but some venomous snakes can pose serious risks.
Signs of a Snake Bite:
- Two puncture wounds at the bite site
- Swelling or discoloration around the wound
- Intense pain or numbness
- Nausea, dizziness, or difficulty breathing in serious cases
First Aid Steps for Snake Bites
- Stay Calm: Panicking increases your heart rate, speeding up venom spread if the snake is venomous. Keep the person as still as possible.
- Identify the Snake (If Safe): Note the snake’s color and size, but do NOT handle it or attempt to kill it.
- Immobilize the Affected Area: Keep the bite site lower than the heart and prevent movement. Wrap it with a bandage (not too tight) to slow venom spread, but don’t use a tourniquet.
- Call Emergency Services: Snake bites, especially venomous ones, require immediate medical treatment. Evacuate the individual or contact rescue services right away.
Prevention Tip: Stick to marked trails, wear sturdy boots, and avoid placing hands or feet in blind spots like logs or tall grass when hiking.
Essential First Aid Kit for Wilderness Adventures
Preparation is half the battle. Here’s a quick list of must-have items for your first aid kit on outdoor trips to help you combat most emergencies effectively:
- Adhesive bandages in various sizes
- Antiseptic wipes and antibiotic ointment
- Electrolyte packets for dehydration
- Space blanket for hypothermia and shelter
- Elastic bandages for sprains or snake bite immobilization
- Tweezers for splinter or tick removal
- Pain relievers (like ibuprofen)
- Anti-allergy medication or an EpiPen for severe reactions
- A whistle and emergency signaling device
Keep your kit sealed and check for expired items before heading out!
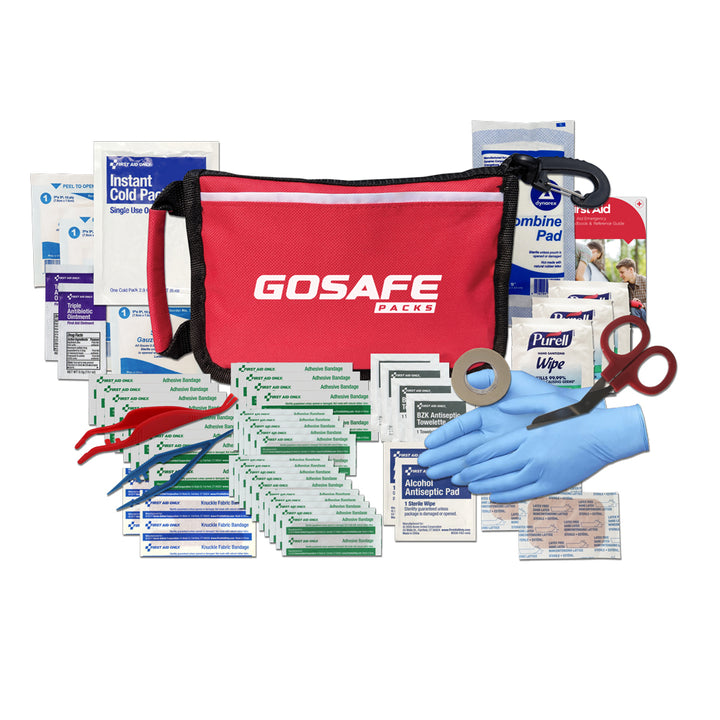
First Aid ReadyMed Pack

$29.95
$35.94
Features: Rugged 600 Denier bag with oversized hook. Compact and portable, it contains essential medical supplies for treating minor injuries and accidents on the go. Perfect for travel, outdoor adventures, and daily use. … read more
Prevention is the Best Medicine
While knowing how to handle emergencies is crucial, prevention always comes first. Here are a few simple tips to help you stay safe outdoors:
- Plan Your Route: Know your trail well, including where to find water sources or potential shelter.
- Pack Essentials: Stick to the “10 Hiking Essentials,” including navigation tools, extra food, and clothing layers.
- Inform Someone: Share your plans with a friend or family member so someone knows your location and return time.
- Check the Weather: Avoid surprises by monitoring conditions in your destination area.
- Practice Situational Awareness: Pay attention to your surroundings, including wildlife, changing environments, and your group’s condition.
Preparedness is Key to Enjoying the Wilderness
Wilderness adventures are a thrilling way to connect with nature, but emergencies can happen even to the most seasoned explorers. By learning key first aid skills for dehydration, hypothermia, and snake bites—and carrying the right gear—you can turn unforeseen challenges into manageable situations.
Remember, safety and readiness go hand in hand. The more you prepare for your trip, the better you can enjoy the beauty of the great outdoors. Pack your gear, trust your training, and set out with confidence.
Happy exploring!