Parenthood is full of joyful milestones, but it can also come with moments of panic—especially when medical emergencies arise. Knowing how to respond in those critical first moments can make all the difference. Whether it's choking, a burn, or an unresponsive infant, equipping yourself with essential first aid skills is a vital step in safeguarding your little one.
This guide will walk you through the basics of infant first aid and empower you with clear, actionable steps to handle emergencies.
Why Infant First Aid Matters
Accidents can happen in an instant. According to the CDC, choking is the leading cause of death in children under age one, while burns and falls can result in serious injuries. Quick and informed action can prevent long-term damage or even save a life. By understanding the fundamentals of infant first aid, you can reframe moments of fear into resolute action.
Whether you're a first responder, a healthcare professional, or a parent, these actionable tips are essential knowledge.
First Aid QuickMed Pack

$24.95
$29.94
Features: Ripstop nylon bag Handy front pocket, durable carabiner and a handle An essential part of any household or workplace. Designed to efficiently treat burns and injuries. Keep your safety a top priority with this comprehensive pack. … read more
Essential First Aid Skills for Infants
1. Responding to Choking
Choking is one of the most common emergencies among infants, as their curiosity leads them to explore their environment by putting objects (or food) into their mouths. Taking immediate action is critical.
Signs of Choking in Infants
- Difficulty breathing or no breathing at all
- Coughing, gagging, or high-pitched sounds
- Skin turning blue (cyanosis)
- No sound but visible struggle to breathe
What to Do if Your Infant is Choking
Follow these steps carefully if your infant is choking and unable to cough it out on their own.
Step 1: Position the Baby
- Place the baby face-down on your forearm, resting their head lower than their chest. Use your thigh or lap to support yourself.
Step 2: Administer Back Blows
- Using the heel of your hand, give 5 firm back blows between the shoulder blades. Ensure the baby’s head is supported.
Step 3: Chest Compressions
- Turn the baby face-up and use two fingers to administer 5 chest compressions in the center of their chest, just below the nipple line.
Repeat until the object is dislodged or the infant becomes unresponsive. If the baby stops breathing, move to CPR (covered below).
2. Treating Burns
Infants' skin is highly sensitive, making them more prone to severe burns more quickly than older children. Immediate first aid can mitigate damage and reduce pain.
Types of Burns and How to Treat Them
- Minor Burns (First Degree)
Cool the affected area using lukewarm water for 10-15 minutes. Cover it with a clean, non-stick dressing. Avoid ice, as it can further damage the skin.
- Severe Burns (Second or Third Degree)
If the burn appears blistered or charred, do not attempt to remove clothing or apply ointments. Cover the area lightly with a sterile, non-stick dressing and seek emergency medical attention immediately.
Note
Never apply butter, creams, or other home remedies to a burn, as they can trap heat and worsen damage.
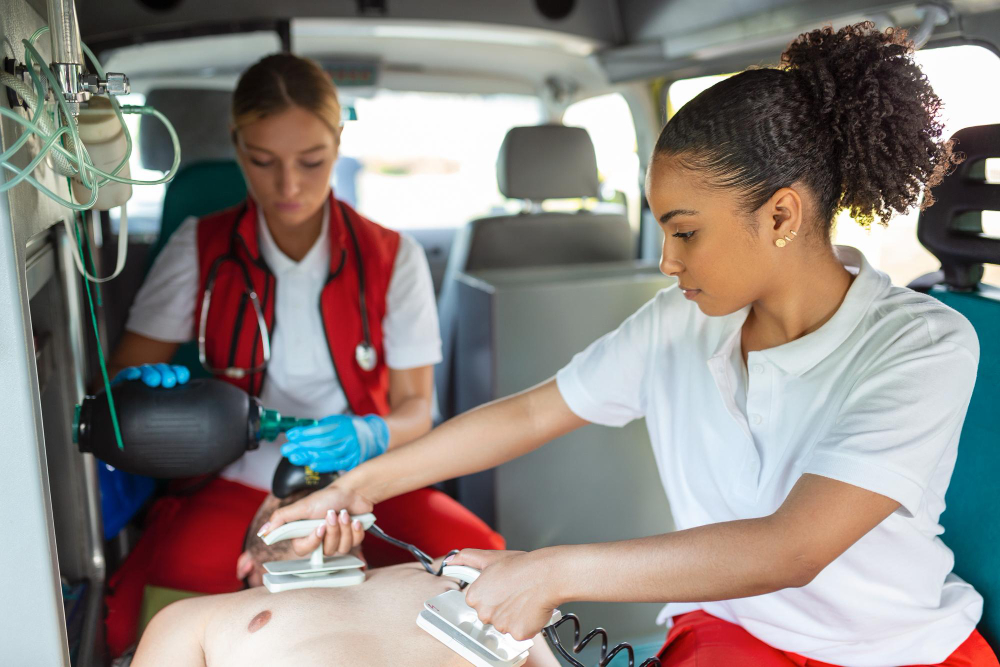
3. Performing Infant CPR
CPR is a life-saving skill that can restore circulation and breathing in critical emergencies such as drowning, choking, or sudden collapse. Performing CPR on infants differs from adults.
Steps for Infant CPR
Step 1: Check Responsiveness and Call for Help
- Gently tap the baby’s foot or shoulder and shout to see if there is any response.
- If unresponsive, immediately call 911 (or your local emergency number). If someone is with you, ask them to call while you begin CPR.
Step 2: Open the Airway
- Tilt the baby’s head back slightly and lift the chin to open the airway.
Step 3: Check for Breathing
- Look for chest movement, listen for breath sounds, and feel for breath on your cheek for no more than 10 seconds.
Step 4: Administer Chest Compressions
- Place two fingers in the center of the chest, just below the nipple line.
- Compress the chest about 1.5 inches deep at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute.
Step 5: Provide Rescue Breaths
- Cover the baby’s nose and mouth with your mouth and give two gentle breaths. Each breath should last about 1 second, just enough to make the chest rise.
Step 6: Continue CPR
- Perform 30 compressions followed by 2 rescue breaths. Repeat until emergency responders arrive or the baby starts breathing.
Tip: Use a timer or count aloud to maintain the pace and cycles accurately.
4. Managing Cuts and Lacerations
Even minor cuts can lead to infections if not treated properly, while deeper wounds may require more urgent care.
Steps to Treat Cuts and Lacerations
- Minor Cuts
Clean the area with lukewarm water, gently pat it dry, and apply an antibiotic ointment. Cover with a sterile bandage.
- Severe Cuts
If the bleeding is heavy and doesn’t stop after 10 minutes of applying firm pressure, seek medical assistance. Keep the area elevated to slow blood flow.
Watch for Signs of Infection
- Redness, swelling, or warmth around the wound
- Discharge of pus
- Fever or increased discomfort
5. Recognizing an Allergic Reaction or Anaphylaxis
Food, insect stings, or medications are common triggers of allergic reactions in infants. Severe reactions can lead to anaphylaxis, a potentially life-threatening condition.
Signs of Anaphylaxis in Infants
- Swelling of the lips, face, or throat
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing
- Hives or rash
- Vomiting or diarrhea
- Sudden, unexplained drowsiness or agitation
How to Respond
- Administer an epinephrine injection (using an EpiPen Jr) if prescribed, and call 911 immediately.
- Lay the baby flat while keeping their legs elevated unless they have trouble breathing.
Building Your Confidence in Infant First Aid
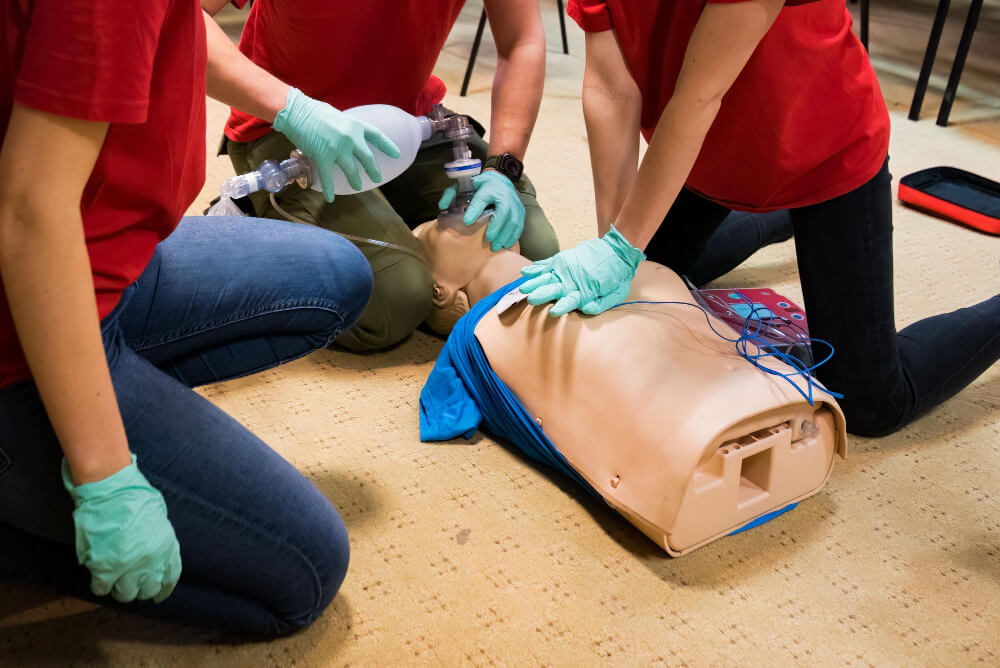
First aid is not just a skill—it’s a confidence booster for parents and caregivers. You don’t have to wait for an emergency to learn. Taking an infant-specific first aid course can prepare you to act decisively in stressful situations.
Organizations like the Red Cross and local hospitals offer certified training programs. Many also include hands-on practice sessions to reinforce your knowledge.
First Aid HomeMed Pack
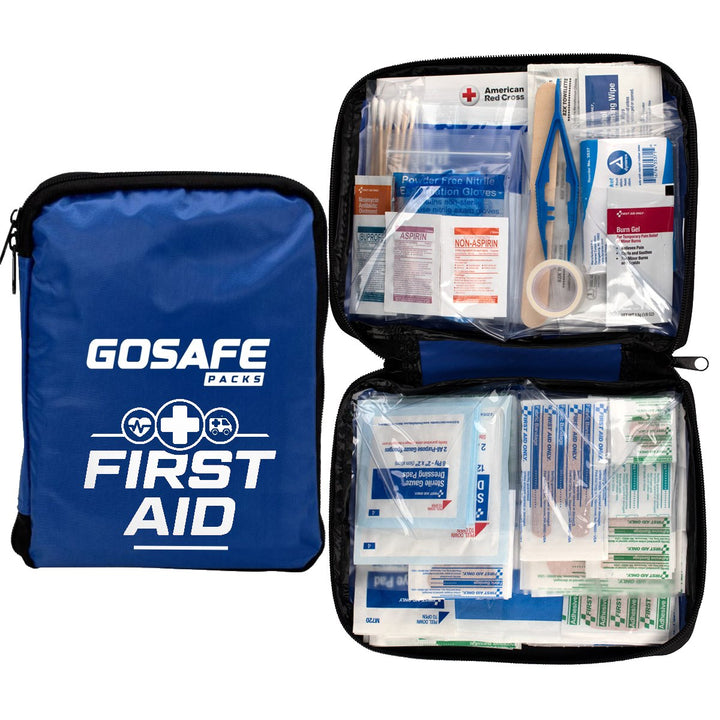
$34.95
$41.94
Features: Stay prepared for emergencies with the HomeMed First Aid Pack. Loaded with essential medical supplies, this kit offers 240 pieces and includes everything you need for an emergency situation. Perfect for families and households. … read more
Empower Yourself with Knowledge
Emergencies involving infants can be one of the most stressful experiences for any caregiver or parent. However, with knowledge and practice, you can approach these moments with the confidence and calmness needed to protect your child.
Equip yourself with these life-saving techniques and share this guide with those in your caregiving circle. And remember, being prepared is the best gift you can give your child—and yourself.