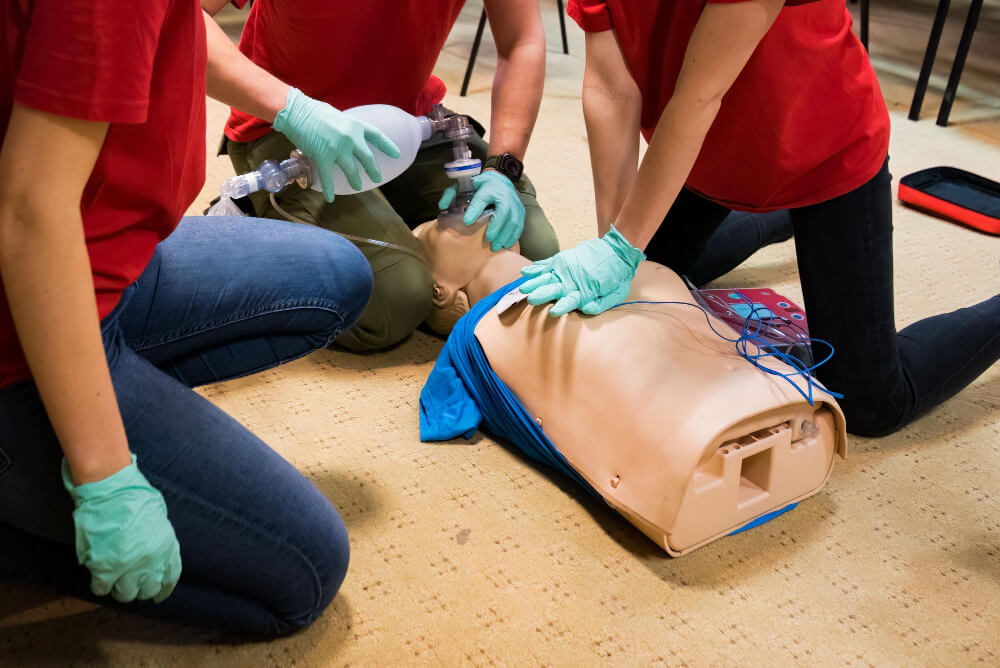
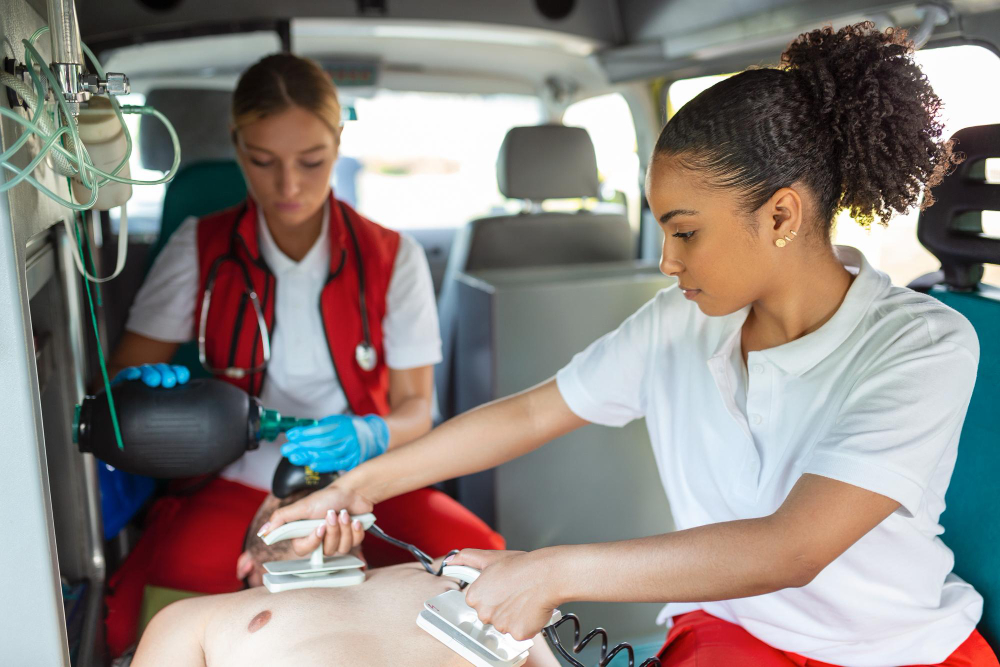
When sudden cardiac arrest strikes, every second counts. The combination of CPR and automated external defibrillators (AEDs) is a lifesaving duo, dramatically increasing the chances of survival. But how exactly do AEDs work alongside CPR to save lives? Whether you’re a first responder, healthcare professional, or just part of the general public who wants to be prepared, understanding the pivotal role of AEDs could one day help you make a life-or-death difference.
This blog will take you through the essentials of how AEDs work, why they’re crucial during cardiac emergencies, and practical ways you can use this knowledge to help save lives.
What is an AED and How Does It Work?
If you’ve seen a small, portable device in public spaces like gyms, airports, or offices with the letters “AED,” you’ve already encountered this powerful life-saving tool. An automated external defibrillator (AED) is a portable medical device designed to deliver an electric shock to the heart when someone experiences sudden cardiac arrest (SCA).
Here’s how AEDs operate step-by-step:
- Detects Heart Rhythm: Once the AED pads are attached to the person’s chest, the device analyzes the heart's rhythm using built-in technology.
- Identifies Need for Shock: If the device detects a dangerous rhythm like ventricular fibrillation (an erratic and chaotic heart rhythm), it determines whether a shock is necessary. If no shock is required, the AED will advise continuing chest compressions and CPR.
- Administers Electric Shock: With clear, automated voice instructions, the AED prompts the user to press a button (in most devices) to deliver an electric shock that resets the heart's rhythm.
This simplicity and automation enable even non-medical personnel to operate an AED with confidence.
First Aid QuickMed Pack

$24.95
$29.94
Features: Ripstop nylon bag Handy front pocket, durable carabiner and a handle An essential part of any household or workplace. Designed to efficiently treat burns and injuries. Keep your safety a top priority with this comprehensive pack. … read more
Why Time Matters Most in Sudden Cardiac Arrest
Sudden cardiac arrest is a time-critical medical emergency. During SCA, the heart suddenly stops pumping blood to the brain and vital organs. Without immediate treatment, death can occur within minutes.
- Survival Odds Drop By 10% Every Minute in cardiac arrest if no resuscitation efforts are made.
- CPR alone provides oxygen to the brain temporarily, but it cannot restore the heart's rhythm to normal. Defibrillation via an AED is the only effective way to correct life-threatening arrhythmias like ventricular fibrillation.
This is why combining CPR with the timely use of an AED is crucial.
How AEDs Complement CPR in Saving Lives
CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) and AEDs form a powerful duo, each playing a specific and complementary role in responding to cardiac arrest.
1. CPR Keeps Blood Moving
The primary role of CPR is to keep oxygen-rich blood circulating to the brain and vital organs when the heart has stopped beating. Chest compressions and rescue breaths maintain some blood circulation and oxygenation until the heart can restart.
2. AED Restores Heart Rhythm
While CPR buys crucial time, it does not treat the underlying arrhythmia causing cardiac arrest. The electric shock delivered by an AED can reset the heart's electrical system, giving it a chance to resume a normal rhythm.
3. The Chain of Survival
International guidelines emphasize the importance of combining both CPR and AED use within the first few moments of cardiac arrest. This is known as the “chain of survival”, which includes:
- Immediate recognition of cardiac arrest and calling for emergency help
- Early CPR to maintain circulation
- Early defibrillation for restoring heart rhythm
- Advanced medical care to address the root cause
Missing any link in this chain dramatically reduces survival rates.
The Impact of AEDs on Survival Rates
The stats don’t lie—AEDs are game-changers in increasing the survival odds:
- AED use within the first 3-5 minutes of cardiac arrest increases survival rates to 50-70%.
- Without an AED, the survival rate for out-of-hospital cardiac arrests plummets to less than 10%.
Equipped communities that make AEDs accessible and teach people how to use them see drastically higher recovery rates.
AED Accessibility Makes a Difference
Countries and organizations that have introduced public access defibrillation (PAD) programs report impressive results. For example:
- A study in Denmark showed that bystander defibrillation (using an AED) doubled survival rates compared to cases where an AED was not used.
- Survival rates in locations with AEDs (like airports or sports stadiums) are significantly higher than in areas without them.
Using an AED: You Can Do It
One of the biggest misconceptions about AEDs is that you need extensive medical training to use one. The reality? AEDs are designed to be simple and intuitive. Most devices offer step-by-step voice prompts that guide the user through the process.
Here’s how you can use an AED with confidence:
- Turn It On: Power the AED on, either by pressing a button or opening the device, depending on the model.
- Attach Pads: Follow the diagrams on the AED pads to place them correctly on the victim's chest (one pad above the right nipple and the other below the left chest).
- Follow Instructions: The AED will analyze the heart rhythm and indicate whether a shock is recommended. Make sure no one is touching the patient before delivering the shock.
Remember, you cannot harm the patient by using an AED. If they don’t need a shock, the AED won’t deliver one.
What If You're Scared?
It’s normal to feel a surge of panic during emergencies, but remember one thing—your quick action can make a life-or-death difference. By combining basic training in CPR with the confidence to use an AED, you're incredibly well-equipped to save a life.
Busting Myths About AEDs
Some people hesitate to use AEDs due to common misconceptions. But the truth is:
- AEDs Can't Make Things Worse: They only deliver shocks to victims in need of defibrillation. If no shock is needed, the AED simply won’t deliver one.
- You Won't Get Sued for Trying to Help: Good Samaritan laws in many countries protect bystanders offering emergency assistance.
- Anyone Can Use AEDs: With automated instructions, AEDs are user-friendly even for those with no prior medical training.
Be Part of the Solution
Ensuring widespread access to AEDs and training more people in CPR are critical steps toward saving lives. You can help by:
- Advocating for AEDs in workplaces, gyms, and community spaces.
- Attending basic CPR and AED training courses through organizations like the American Heart Association or Red Cross.
- Encouraging family and friends to become familiar with AEDs.
Together, small individual actions can lead to a dramatic impact on survival rates in emergencies.
First Aid ProMed Pack

$39.95
$47.94
Features: Be ready for any emergency with the GoSafe ProMed First Aid Pack. Rip Stop Nylon zippered bag Fully equipped with top-quality medical supplies to handle injuries and accidents Safety and peace of mind, always within reach. … read more
Why Knowledge Is Power in Cardiac Emergencies
By now, you understand the paramount importance of AEDs and CPR in saving lives during cardiac arrests. These tools aren’t just for first responders or healthcare professionals—every member of the public can (and should) play a role in responding to cardiac emergencies.
Want to become more confident in using AEDs and performing CPR? Start by exploring local training courses and ensuring AED accessibility in your community or workplace. Together, we can create safer, heart-smart communities where everyone is prepared to act.