Whether it’s an adventurous hike, a fun day at the park with your pet, or a family outing in the backyard, life’s simplest joys often bring nature's surprises. Yet, one not-so-pleasant surprise is the occasional encounter with bites and stings from animals, insects, or plants. Knowing how to effectively handle these situations can make all the difference in not just easing discomfort, but also preventing complications.
This guide is tailored for pet owners, outdoor enthusiasts, and parents. It will walk you through understanding the risks, providing immediate first aid, recognizing when medical help is necessary, and taking steps to prevent bites and stings altogether. By the end, you’ll feel better prepared to handle whatever creatures come your way.
First Aid QuickMed Pack

$24.95
$29.94
Features: Ripstop nylon bag Handy front pocket, durable carabiner and a handle An essential part of any household or workplace. Designed to efficiently treat burns and injuries. Keep your safety a top priority with this comprehensive pack. … read more
Understanding the Risks
Not all bites and stings are created equal—and not all come from the same sources. Whether it’s a curious pet getting too close to a bee or a child unknowingly stepping on an anthill, here’s what you need to know about common culprits:
Common Animals That Bite
- Dogs and Cats: Pet bites happen, even from animals you trust. Dogs may nip out of overexcitement, while cats might scratch and bite as a defense mechanism.
- Wild Animals: Squirrels, raccoons, bats, and snakes are known for unexpected bites, particularly when threatened or provoked.
- Marine Creatures: Jellyfish, sea urchins, and stingrays can deliver painful stings in the ocean.
Common Stinging and Biting Insects
- Bees, Wasps, and Hornets: Their venom can cause swelling and allergic reactions, with wasps being particularly aggressive.
- Ticks: These tiny creatures latch onto the skin and can transmit diseases such as Lyme disease.
- Mosquitoes and Ants: Though often less severe, their bites still cause itching and irritation.
Plants That Can Cause Reactions
- Some plants like poison ivy, oak, or sumac contain oils that irritate the skin and mimic sting-like symptoms. Being aware of these in your area is crucial.
Knowing what you’re dealing with and where these threats are likely to occur—such as forests, beaches, or your own yard—can help you identify the source and treat it appropriately.
First Aid Basics
Providing immediate care is critical when dealing with bites and stings. Following these general steps will help minimize pain, inflammation, and the risk of infection:
Step 1: Stay Calm and Assess the Situation
- Remove yourself or the affected individual from the source of the bite or sting.
- Keep the person still to slow down the spread of venom or bacteria.
Step 2: Clean the Affected Area
- For bites or stings, wash the area gently with soap and water to remove debris, bacteria, or venom.
- If a stinger (like a bee stinger) is visible, scrape it off carefully using the edge of a card; avoid using tweezers, as squeezing might release more venom.
Step 3: Manage Swelling and Pain
- Apply a cold compress or ice wrapped in a cloth to reduce swelling and numb the pain.
- Elevate the affected area if possible.
Step 4: Apply Topicals
- Over-the-counter hydrocortisone creams or antihistamines like Benadryl can alleviate itching and swelling for insect stings.
- For bites, an antibiotic ointment can help prevent infection.
Step 5: Monitor for Reactions
- Keep an eye out for worsening symptoms such as excessive swelling, difficulty breathing, or signs of infection like redness and warmth.
These steps can greatly alleviate immediate discomfort and help manage the situation until further treatment is available, if necessary.
Special Considerations for Pets and Children
Pets and children are especially vulnerable to bites and stings due to their curiosity and smaller body size. Here’s how you can address their unique needs:
For Pets
- Identify the Problem: Pet bites can come from domestic animals (including play fights) or wild animals during outdoor activities.
- Immediate Care: If your pet has been stung, check for signs like excessive licking, swelling, or scratching. Wash the area gently and apply a pet-safe antiseptic.
- Beware of Allergies: Some pets, particularly certain dog breeds, are extremely allergic to stings. Symptoms include vomiting, swelling around the face, and difficulty breathing. Seek veterinary help immediately.
For Children
- Recognize Symptoms: Children might not always express discomfort clearly. Look for behavioral clues, such as reluctance to use the affected limb or fidgeting.
- Use Gentle Care: Children’s skin can be more sensitive, so avoid harsh antiseptics. Use cool compresses and mild antihistamines suited for their age.
- Comfort First: Bites and stings can be frightening for kids. Reassure them, and try to create a distraction while performing first aid.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many bites and stings can be treated at home, some require medical intervention. Here’s when you should visit a doctor or vet:
- Severe Allergic Reactions
Symptoms like difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or hives indicate an anaphylactic reaction requiring immediate care. Use an EpiPen if available.
- Signs of Infection
Redness, warmth, swelling, and pus are signs that a bite or sting has become infected and needs antibiotics.
- Unusual Symptoms
If the affected individual develops fever, fatigue, or joint pain after a tick bite, Lyme disease could be the cause.
- Bites from Wild or Stray Animals
Any bite from an unvaccinated animal, bat, or raccoon requires immediate medical care to rule out rabies.
- Excessive Bleeding
Deep animal bites, especially from dogs or wild animals, should be treated promptly to stop bleeding and ensure proper wound care.
Being aware of these red flags can make a critical difference in ensuring safety and health for you, your family, and your furry companions.
Preventing Bites and Stings
Prevention is always better than cure, and there are several steps you can take to reduce the risk of bites and stings:
- Use Repellents
Apply insect repellents with DEET and consider citronella or eucalyptus sprays for eco-friendly options.
- Dress Smart
Wear long sleeves, long pants, and closed-toe shoes when exploring wilderness areas. Light colors make it easier to spot insects.
- Practice Awareness
Teach children not to disturb animals, and check your yard for nests or hives frequently. Pet owners should ensure playtime with other pets is monitored.
- Address Vulnerable Spaces
Secure trash cans tightly to deter wildlife and inspect wooden areas for termite activity.
- Maintain a First Aid Kit
Always carry a first aid kit stocked with bandages, antiseptics, and medication whenever heading outdoors.
These proactive steps can significantly lower your chances of encountering painful bites and stings.
First Aid ProMed Pack
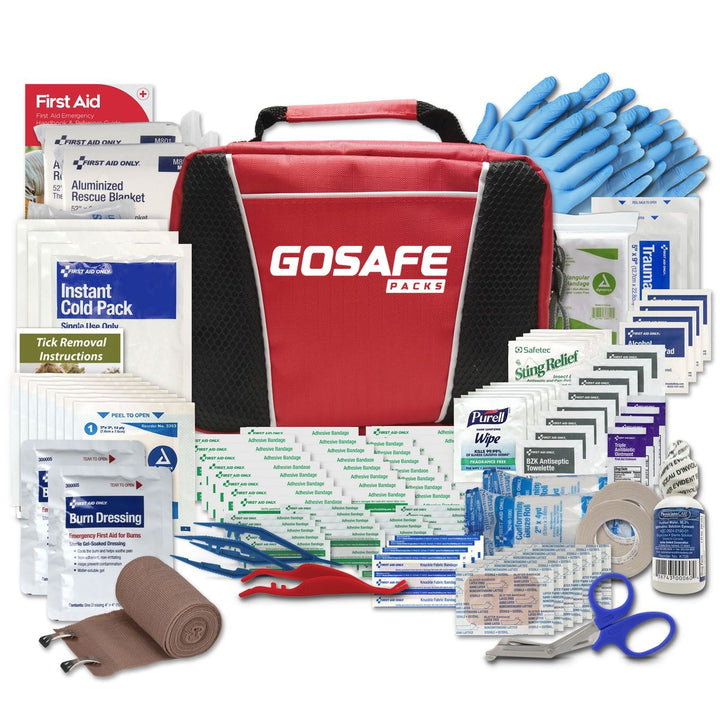

$39.95
$47.94
Features: Be ready for any emergency with the GoSafe ProMed First Aid Pack. Rip Stop Nylon zippered bag Fully equipped with top-quality medical supplies to handle injuries and accidents Safety and peace of mind, always within reach. … read more
Preparedness is Your Best Protection
From curious pets to unexpected wildlife encounters, knowing how to handle bites and stings is an essential skill for anyone who spends time outdoors. With the steps outlined in this guide, you can quickly address incidents, prevent complications, and protect yourself and your loved ones.
For more safety tips and first aid advice, share this article with friends and family. The more prepared we are, the safer everyone can be! Stay safe out there.