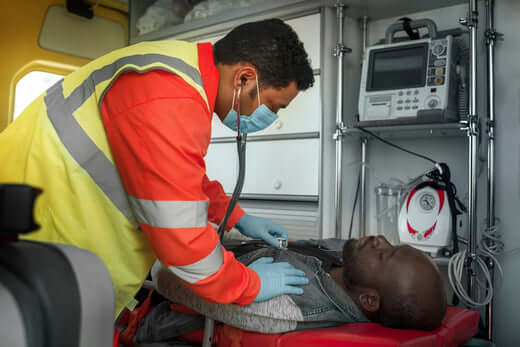
Picture this: you're at home, enjoying a quiet evening when suddenly, your child starts choking or a loved one experiences a severe allergic reaction. Would you know what to do? Medical emergencies can be overwhelming, but knowing how to act quickly and effectively can make all the difference in saving a life.
This comprehensive guide is designed to help parents, caregivers, and first aid enthusiasts prepare for and respond to emergencies with confidence. By the end, you'll have practical steps to take during critical situations—and the motivation to seek further first aid training for added preparedness.
Understanding Medical Emergencies
What Are Medical Emergencies?
A medical emergency is any life-threatening situation that requires immediate action to prevent serious injury or death. These events can happen anytime, anywhere, and often when least expected—especially in households with children or elderly individuals.
Examples of Common Medical Emergencies
Some of the most frequent emergencies include:
- Choking: When an object blocks the airway, preventing normal breathing.
- Burns: Caused by heat, chemicals, or electrical accidents.
- Severe Allergic Reactions (Anaphylaxis): Often triggered by food, insect stings, or medications.
- Heart Attacks or Stroke: Sudden onset of symptoms signaling cardiac or brain-related issues.
- Uncontrolled Bleeding: Profuse bleeding from injuries like deep cuts or wounds.
Understanding common emergencies is the first step to tackling them effectively.
First Aid QuickMed Pack

$24.95
$29.94
Features: Ripstop nylon bag Handy front pocket, durable carabiner and a handle An essential part of any household or workplace. Designed to efficiently treat burns and injuries. Keep your safety a top priority with this comprehensive pack. … read more
Preparing for Emergencies
Preparation is key to handling emergencies calmly. Even small proactive steps can make a big difference.
Be Equipped with a First Aid Kit
Every home should have a well-stocked first aid kit. Essential items include:
- Adhesive bandages, gauze, and medical tape
- Antiseptic wipes and ointment
- Tweezers for removing splinters or debris
- Thermometer and disposable gloves
- Pain relievers and antihistamines
- A first aid manual for quick reference
Check your kit regularly to ensure nothing has expired or run out.
Create an Emergency Contact List
Keep a visible list of emergency contacts, such as:
- Local 911 or emergency services
- Poison Control (1-800-222-1222 in the U.S.)
- Pediatrician, family doctor, or specialist
- Trusted neighbors or nearby family members
Save these contacts in your phone—just in case grabbing a physical list isn’t feasible in the moment.
Develop an Emergency Plan
Work with your household to determine roles and protocols during an emergency. For example, assign one person to call 911 while others assist directly with the patient or guide emergency responders to your location.
Immediate Response to an Emergency
When faced with a medical emergency, staying calm is critical. Here’s a step-by-step overview of how to take immediate, effective action.
Step 1: Assess the Situation
- Safety First: Ensure the scene is safe for you and the patient.
- Check Responsiveness: Look for signs of consciousness. Speak to the person and gently tap their shoulder.
- Observe for Dangers: Assess hazards such as fire, broken glass, or exposed electrical cords.
Step 2: Perform Basic First Aid
CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation)
If someone isn't breathing or has no pulse:
- Position the patient on their back on a firm, flat surface.
- Place your hands over their chest and push hard and fast—approximately 100–120 compressions per minute.
- If trained, alternate chest compressions with rescue breaths (30 compressions, then two breaths).
For untrained bystanders, focus on just chest compressions until help arrives.
The Heimlich Maneuver (for Choking)
- For adults or children:
- Stand behind the person and wrap your arms around their waist.
- Make a fist with one hand and place it slightly above their navel.
- Grasp your fist with the other hand and press inward and upward with a quick, forceful motion.
Always remember to seek professional medical care afterward, even if the object is successfully expelled.
Control Severe Bleeding
- Apply firm pressure to the wound with a clean cloth or gauze.
- If available, elevate the injured area above the heart to slow bleeding.
- Secure the dressing tightly with medical tape or a bandage.
Act decisively—time is of the essence!
Communicating with Emergency Services
When calling 911 or other emergency services, how you communicate can be vital.
What to Share with the Operator:
- Your Location: Be as specific as possible, including landmarks.
- The Nature of the Emergency: Describe what’s happened and the patient’s condition (e.g., "They are unconscious but breathing").
- Your Actions: Detail any first aid you've already administered and any medical history you’re aware of.
Stay on the line until the operator confirms you can hang up.
Pro tip: Practice mock emergency calls with your household. Familiarity breeds confidence.
Handling Specific Emergencies
Each emergency demands unique actions. Here’s how to address some of the most common ones in detail:
Burns
- Minor Burns: Cool the affected area under lukewarm water and cover with non-stick gauze.
- Severe Burns: Avoid breaking blisters. Call 911 and wrap the area loosely with a clean cloth.
Cuts and Lacerations
- Clean the wound with mild soap and water.
- Apply an antibiotic ointment before bandaging.
- Elevate the area if there’s heavy bleeding.
Choking
- Follow the Heimlich maneuver instructions mentioned earlier. For infants, use gentle back blows and chest compressions instead.
Allergies
- If the person has an Epinephrine Auto Injector (epi-pen), administer it immediately.
- Stay with them until professional help arrives.
Practice these responses frequently to ensure muscle memory kicks in when it matters most.
Post-Emergency Care
Once the immediate crisis is under control:
- Monitor the Patient: Continue checking for changes in breathing, consciousness, or pain levels.
- Follow Medical Advice: Always consult with healthcare professionals after an emergency, even if symptoms improve.
- Reflect and Restock: Take stock of your response. Is your first aid kit depleted? Are there steps you could improve?
Prevent trauma by staying composed and reassuring the patient throughout.
First Aid HomeMed Pack
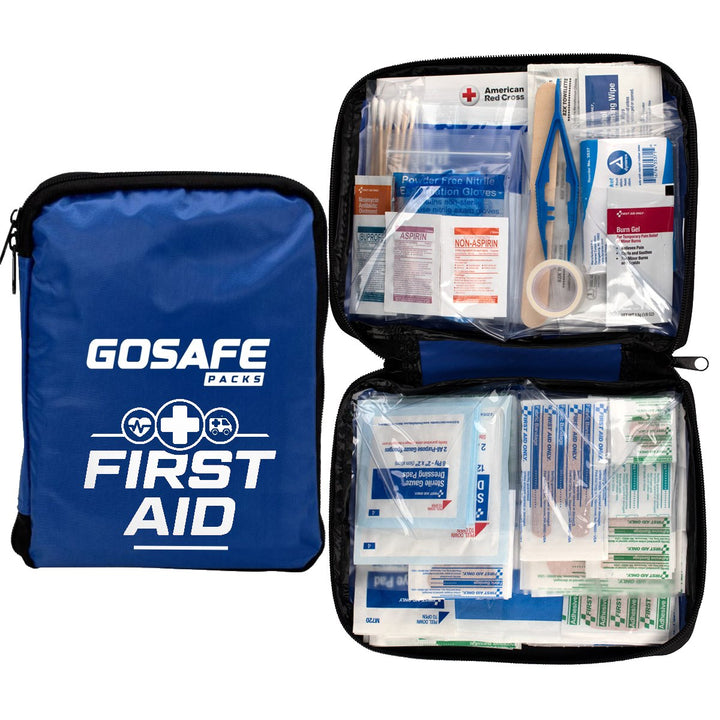
$34.95
$41.94
Features: Stay prepared for emergencies with the HomeMed First Aid Pack. Loaded with essential medical supplies, this kit offers 240 pieces and includes everything you need for an emergency situation. Perfect for families and households. … read more
Empower Yourself and Your Community
Handling medical emergencies isn’t about being fearless—it’s about being prepared. By understanding common emergencies, creating a plan, and gaining first aid skills, you can act decisively when the moment arises.
Want to go a step further? Consider taking a certified first aid course. Programs from organizations like the American Red Cross or the National CPR Foundation equip you with life-saving skills and the confidence to lead in emergencies. Encourage friends, family, and neighbors to do the same—because safety is a shared responsibility.
Every second counts during an emergency. Prepare today so that you’ll be ready to act when it truly matters.