Spending time outdoors is a joy—you connect with nature, enjoy fresh air, and get some exercise. But, the downside? The occasional sting or bite. Bee stings and bug bites are common nuisances for outdoor enthusiasts, parents, and nature lovers alike. Though they often get lumped together, they're very different in cause, symptoms, and treatment.
Being able to identify whether you're dealing with a bee sting or bug bite and knowing how to treat it effectively can save you discomfort and even potential complications. This guide will walk you through the differences and provide actionable advice on how to handle each one so you can get back to enjoying the great outdoors.
The Basics of Bee Stings
If you’ve been stung by a bee, you’ll know that it’s not something you’d soon forget. Understanding the specifics of bee stings can help you act swiftly and properly.
What Happens When a Bee Stings?
A bee sting occurs when a bee injects venom into your skin through its stinger, a tiny barbed needle. Honeybees leave their stinger behind, which continues to pump venom into your skin until it’s removed. Other bees, like wasps or bumblebees, do not lose their stinger and can sting multiple times.
First Aid MiniMed Pack

$19.95
$23.94
Features: Comprehensive and essential kit for any medical emergency. Contains all the necessary supplies to tend to minor injuries and prevent their progression. Have peace of mind knowing you're prepared for any unexpected situation. … read more
Appearance of a Bee Sting
- A red, swollen welt usually forms at the sting site.
- You may see a white center, which is where the stinger penetrated your skin.
- For honeybees, the stinger itself may still be embedded.
Symptoms of Bee Stings
- Pain or a burning sensation at the sting site.
- Redness and swelling.
- Itching around the affected area.
- Severe reactions, though rare, include difficulty breathing, dizziness, or swelling in areas not near the sting site—potential signs of an allergic reaction requiring immediate medical attention.
How to Treat a Bee Sting
If you’ve been stung by a bee, quick and proper treatment can mitigate discomfort and swelling.
- Remove the Stinger
- Use a flat edge (like a credit card) to scrape the stinger out. Avoid using tweezers, as squeezing the stinger can release more venom.
- Clean the Area
- Wash the sting site with soap and water to prevent infection.
- Apply a Cold Compress
- Use ice or a cold pack to reduce swelling and numb pain.
- Use OTC Remedies
- Anti-itch creams, hydrocortisone cream, or oral antihistamines can help minimize itching and discomfort.
- Monitor for Severe Reactions
- If the person stung experiences difficulty breathing or swelling that extends beyond the sting, seek medical help immediately.
The Basics of Bug Bites
Bug bites are more common than bee stings and come in a dizzying variety, depending on the insect doing the biting—mosquitoes, spiders, fleas, and ticks, to name just a few.
What Happens When a Bug Bites?
When a bug bites, it either extracts blood (like mosquitoes) or reacts defensively by injecting toxins. The saliva or venom from the bug interacts with your skin, causing irritation, swelling, and an immune response.
Appearance of Bug Bites
Bug bites vary widely in appearance, but here are some general signs to look for:
- Small red dots or welts, sometimes clustered together.
- Mosquito bites are typically small, raised, and itchy with a distinctive round red bump.
- Spider bites may feature two small puncture marks, often surrounded by redness or swelling.
- Tick bites may appear as small red dots, often with a tick still attached.
Symptoms of Bug Bites
- Localized Symptoms
- Itching, mild redness, and swelling.
- Spider bites might additionally cause blistering or pain.
- Systemic Symptoms
- Symptoms like fever, muscle aches, or a rash might indicate Lyme disease (from tick bites) or an allergic reaction.
How to Treat Bug Bites
While treatment for bug bites depends on the insect, these general steps will help in most cases.
- Clean the Bite Area
- Gently wash with soap and water to prevent infection.
- Apply a Cold Compress
- Reduce swelling and inflammation with a cold pack.
- Use Anti-itch Solutions
- Apply calamine lotion or an antihistamine cream. Oral antihistamines can also help reduce itching.
- Remove Ticks Promptly
- Use fine-tipped tweezers to grasp the tick as close to the skin’s surface as possible and pull upward steadily. Clean the area thoroughly afterward.
- Look for Infection or Severe Reactions
- If the bite shows signs of infection (pus, expanding redness) or comes with flu-like symptoms after a tick bite, see a doctor right away.
Key Differences Between Bee Stings & Bug Bites
Category | Bee Stings | Bug Bites |
|---|---|---|
Cause | Bee injects venom through a stinger. | Bug saliva or toxin interacts with skin. |
Appearance | Red welt with central white spot, may see stinger. | Red lump, clustered bumps, or small punctures. |
Symptoms | Instant pain, swelling, redness. | Itchiness, mild swelling, may vary by bug. |
Risk of Allergies | Higher for bee stings (anaphylaxis risk). | Rare, unless bitten by specific spiders or ticks. |
Preventing Bee Stings and Bug Bites
Prevention is always better than cure, especially when you’re planning outdoor activities. Here are some practical tips to stay sting-free and bite-free.
Avoiding Bee Stings
- Avoid wearing bright colors and floral prints, which can attract bees.
- Skip sweet-smelling perfumes or lotions.
- Stay calm around bees—fast movements can agitate them.
- Wear protective clothing like long sleeves when in known bee-prone areas.
Avoiding Bug Bites
- Apply insect repellent containing DEET or picaridin, especially during dawn and dusk when mosquitoes are most active.
- Wear long-sleeved shirts and pants while hiking or camping.
- Use mosquito nets or screens in sleeping areas.
- Check yourself and others for ticks after spending time in wooded or grassy areas.
Know When to Call for Help
While most bee stings and bug bites are minor nuisances, certain situations require urgent medical attention. Here’s what to watch for:
- Severe Allergic Reactions
- Symptoms like difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or a rapid heartbeat indicate anaphylaxis and need immediate medical care.
- Signs of Infection
- Redness spreading outward, warmth at the bite or sting site, or pus may be infection symptoms.
- Tick-related Illness
- If flu-like symptoms occur after a tick bite, consult a doctor—they could indicate Lyme disease.
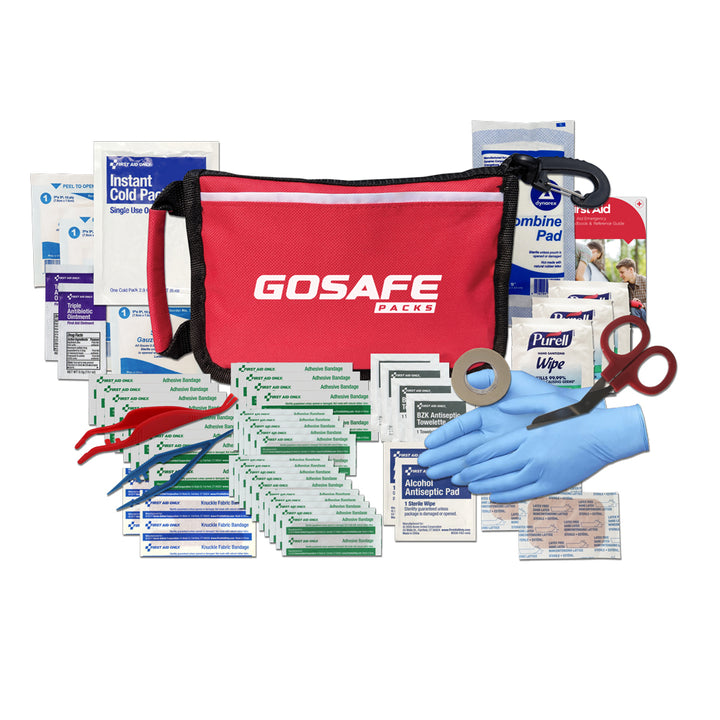
First Aid ReadyMed Pack

$29.95
$35.94
Features: Rugged 600 Denier bag with oversized hook. Compact and portable, it contains essential medical supplies for treating minor injuries and accidents on the go. Perfect for travel, outdoor adventures, and daily use. … read more
Enjoy the Outdoors Safely
Bee stings and bug bites are part of spending time outside—but they don’t have to ruin your day. By learning to identify the culprit and treating it effectively, you ensure a quick recovery and a return to enjoying all the beauty nature has to offer.
Equip yourself with insect repellents, basic first aid knowledge, and a keen eye to spot potential threats. Remember, a little preparation goes a long way toward stress-free outdoor adventures.
Now that you know how to tackle stings and bites, how about planning your next camping trip? Don’t forget your first-aid kit!